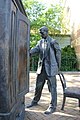Portal:Literature
Introduction
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose, fiction, drama, poetry, and including both print and digital writing. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include oral literature, much of which has been transcribed. Literature is a method of recording, preserving, and transmitting knowledge and entertainment, and can also have a social, psychological, spiritual, or political role.
Literature, as an art form, can also include works in various non-fiction genres, such as biography, diaries, memoir, letters, and essays. Within its broad definition, literature includes non-fictional books, articles or other written information on a particular subject. (Full article...)
General images -
-
The scene in Botticelli's Madonna of the Book (1480) reflects the presence of books in the houses of richer people in his time. (from History of books)
-
Photograph of a printing press in Egypt, c. 1922 (from History of books)
-
The New England Primer (from Children's literature)
-
Statue of C. S. Lewis in front of the wardrobe from his Narnia book The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe (from Children's literature)
-
The Violet Fairy Book (1906)
-
Number of children's books titles published by the trade sector in 2020 (from Children's literature)
-
Statuta Mutine Reformata, 1420–1485; parchment codex bound in wood and leather with brass plaques worked the corners and in the center, with clasps. (from Medieval literature)
-
French author Albert Camus was the first African-born writer to receive the award. (from Nobel Prize in Literature)
-
In 1901, French poet and essayist Sully Prudhomme (1839–1907) was the first person to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature, "in special recognition of his poetic composition, which gives evidence of lofty idealism, artistic perfection, and a rare combination of the qualities of both heart and intellect." (from Nobel Prize in Literature)
-
An early Mexican hornbook pictured in Tuer's History of the Horn-Book, 1896. (from Children's literature)
-
Newbery's A Little Pretty Pocket-Book, originally published in 1744 (from Children's literature)
-
European output of printed books c. 1450–1800 (from History of books)
-
The former Canadian Parliamentary Poet Laureate George Elliott Clarke (2015) (from Canadian literature)
-
Hugo Ball performing at the Cabaret Voltaire (from Performance poetry)
-
The European fairy tale Little Red Riding Hood and the Wolf in a painting by Carl Larsson in 1881. (from Fairy tale)
-
Short story writer Alice Munro won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 2013. (from Canadian literature)
-
J. K. Rowling reads from her novel Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone (from Children's literature)
-
Page from the Blue Quran manuscript, ca. 9th or 10th century CE (from History of books)
-
European output of manuscripts 500–1500 (from History of books)
-
Father Frost acts as a donor in the Russian fairy tale Father Frost, testing the heroine before bestowing riches upon her (from Fairy tale)
-
Ivan Bilibin (1876-1942)'s illustration of the Russian fairy tale about Vasilisa the Beautiful (from Fairy tale)
-
A 15th-century Incunable. Notice the blind-tooled cover, corner bosses, and clasps. (from History of books)
-
A Sumerian clay tablet, currently housed in the Oriental Institute at the University of Chicago, inscribed with the text of the poem Inanna and Ebih by the priestess Enheduanna, the first author whose name is known
-
Goethe's Italian Journey between September 1786 and May 1788 (from Travel literature)
-
Dresden Codex (page 49) (from History of books)
-
Jikji, Selected Teachings of Buddhist Sages and Seon Masters, the earliest known book printed with movable metal type, 1377. Bibliothèque Nationale de France, Paris. (from History of books)
-
Postal stamp of Russia celebrating children's books. (from Children's literature)
-
Folio from a manuscript of the Shanamah (Book of Kings) (from History of books)
-
Woman holding wax tablets in the form of the codex. Wall painting from Pompeii, before 79 CE. (from History of books)
-
Walter Crane's chromolithograph illustration for The Frog Prince, 1874. (from Children's literature)
-
Statue of Minnie the Minx, a character from The Beano. Launched in 1938, the comic is known for its anarchic humour, with Dennis the Menace appearing on the cover. (from Children's literature)
-
Gabrielle Roy was a notable French Canadian author. (from Canadian literature)
-
The Codex Manesse, a German book from the Middle Ages (from History of books)
-
The character which means "poetry", in the ancient Chinese Great Seal script style. The modern character is 詩/诗 (shī). (from History of poetry)
-
Illustration from Robert Louis Stevenson's 1883 pirate adventure Treasure Island (from Children's literature)
-
12-metre-high (40 ft) stack of books sculpture at the Berlin Walk of Ideas, commemorating the invention of modern book printing (from History of books)
-
A mother reads to her children, depicted by Jessie Willcox Smith in a cover illustration of a volume of fairy tales written in the mid to late 19th century. (from Children's literature)
-
A late 18th-century reprint of Orbis Pictus by Comenius, the first children's picture book. (from Children's literature)
-
Illustration from Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, 1865 (from Children's literature)
-
Kings' Fairy Tale, 1909, by Mikalojus Konstantinas Čiurlionis (from Fairy tale)
-
Cutlery for children. Detail showing fairy-tale scenes: Snow White, Little Red Riding Hood, Hansel and Gretel. (from Fairy tale)
-
The first page of Beowulf (from Medieval literature)
-
Estimated medieval output of manuscripts in terms of copies (from Medieval literature)
-
Page from a Jain manuscript depicting the birth of Mahavira, c. 1400 (from History of books)
-
Pages from the 1819 edition of Kinder- und Haus-Märchen by the Brothers Grimm (from Children's literature)
-
H. O. Tanager performs at a bookstore in Boise, Idaho. (from Performance poetry)
-
Hemingway's telegram in 1954 (the academy has alternately used for Literature and in Literature over the years, the latter becoming the norm today) (from Nobel Prize in Literature)
-
Roberto Bolaño is considered to have had the greatest United States impact of any post-Boom author (from Latin American literature)
-
Willy Wonka (from Roald Dahl's Charlie and the Chocolate Factory), and the Mad Hatter (from Lewis Carroll's Alice's Adventures in Wonderland) in London (from Children's literature)
-
1900 edition of the controversial The Story of Little Black Sambo (from Children's literature)
-
An author portrait of Jean Miélot writing his compilation of the Miracles of Our Lady, one of his many popular works. (from History of books)
-
The Crescent Moon by Rabindranath Tagore illus. by Nandalal Bose, Macmillan 1913 (from Children's literature)
-
The Story of Mankind (1921) by Hendrik van Loon, 1st Newbery Award winner (from Children's literature)
-
A Tagore illustration of a Hindu myth (from Children's literature)
-
A poet with a few enraptured fans (from Performance poetry)
-
European output of books 500–1800 (from History of books)
-
Sculpture of Alfonso Reyes writer of influential pieces of Mexican surrealism. (from Latin American literature)
-
The Adventures of Pinocchio (1883) is a canonical piece of children's literature and one of the best-selling books ever published. (from Children's literature)
-
Handwritten notes by Christopher Columbus on a Latin edition of The Travels of Marco Polo (from Travel literature)
-
Natias Neutert performing Diogenes Synopsis as at Künstlerhaus Bethanien Berlin, 1986 (from Performance poetry)
-
The Book of the Dead of Hunefer, c. 1275 BCE, ink and pigments on papyrus, in the British Museum (London) (from History of books)
-
Charles G. D. Roberts was a poet that belonged to an informal group known as the Confederation Poets. (from Canadian literature)
-
Gabriel García Márquez, one of the most renowned Latin American writers (from Latin American literature)
-
A Chinese bamboo book (from History of books)
-
Peruvian poet César Vallejo, considered by Thomas Merton "the greatest universal poet since Dante" (from Latin American literature)
-
Octavio Paz helped to define modern poetry and the Mexican personality. (from Latin American literature)
-
John Bauer's illustration of trolls and a princess from a collection of Swedish fairy tales (from Fairy tale)
-
Folio from the Shah Jahan Album, c. 1620, depicting the Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan (from History of books)
Candide, ou l'Optimisme is a French satire first published in 1759 by Voltaire, a philosopher of the Age of Enlightenment. It begins with a young man, Candide, who is living a sheltered life in an Edenic paradise and being indoctrinated with Leibnizian optimism (or simply Optimism) by his mentor, Pangloss. The work describes the abrupt cessation of this lifestyle, followed by Candide's slow, painful disillusionment as he witnesses and experiences great hardships in the world. Voltaire concludes with Candide, if not rejecting optimism outright, advocating a deeply practical precept, "we must cultivate our garden", in lieu of the Leibnizian mantra of Pangloss, "all is for the best in the best of all possible worlds".
Candide is characterised by its sarcastic tone, as well as by its erratic, fantastical and fast-moving plot. A picaresque novel with a story similar to that of a more serious bildungsroman, it parodies many adventure and romance clichés, the struggles of which are caricatured in a tone that is mordantly matter-of-fact. Still, the events discussed are often based on historical happenings, such as the Seven Years' War and the 1755 Lisbon earthquake. As philosophers of Voltaire's day contended with the problem of evil, so too does Candide in this short novel, albeit more directly and humorously. Voltaire ridicules religion, theologians, governments, armies, philosophies, and philosophers through allegory; most conspicuously, he assaults Leibniz and his optimism.
-
Lie Kim Hok (Chinese: 李金福; pinyin: Lǐ Jīnfú; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: Lì Kim-hok; 1 November 1853 – 6 May 1912) was a peranakan Chinese teacher, writer, and social worker active in the Dutch East Indies and styled the "father of Chinese Malay literature". Born in Buitenzorg (now Bogor), West Java, Lie received his formal education in missionary schools and by the 1870s was fluent in Sundanese, vernacular Malay, and Dutch, though he was unable to understand Chinese. In the mid-1870s he married and began working as the editor of two periodicals published by his teacher and mentor D. J. van der Linden. Lie left the position in 1880. His wife died the following year. Lie published his first books, including the critically acclaimed syair (poem) Sair Tjerita Siti Akbari and grammar book Malajoe Batawi, in 1884. When van der Linden died the following year, Lie purchased the printing press and opened his own company.
Over the following two years Lie published numerous books, including Tjhit Liap Seng, considered the first Chinese Malay novel. He also acquired printing rights for Pembrita Betawi, a newspaper based in Batavia (now Jakarta), and moved to the city. After selling his printing press in 1887, the writer spent three years working in various lines of employment until he found stability in 1890 at a rice mill operated by a friend. The following year he married Tan Sioe Nio, with whom he had four children. Lie published two books in the 1890s and, in 1900, became a founding member of the Chinese organisation Tiong Hoa Hwee Koan, which he left in 1904. Lie focused on his translations and social work for the remainder of his life, until his death from typhus at age 58. (Full article...) -
Ezra Morgan Meeker (December 29, 1830 – December 3, 1928) was an American pioneer who traveled the Oregon Trail by ox-drawn wagon as a young man, migrating from Iowa to the Pacific Coast. Later in life he worked to memorialize the Trail, repeatedly retracing the trip of his youth. Once known as the "Hop King of the World", he was the first mayor of Puyallup, Washington.
Meeker was born in Butler County, Ohio, to Jacob and Phoebe Meeker. His family relocated to Indiana when he was a boy. He married Eliza Jane Sumner in 1851; the following year the couple, with their newborn son and Ezra's brother, set out for the Oregon Territory, where land could be claimed and settled on. Although they endured hardships on the Trail in the journey of nearly six months, the entire party survived the trek. Meeker and his family briefly stayed near Portland, then journeyed north to live in the Puget Sound region. They settled at what is now Puyallup in 1862, where Meeker grew hops for use in brewing beer. By 1887, his business had made him wealthy, and his wife built a large mansion for the family. In 1891, an infestation of hop aphids destroyed his crops and took much of his fortune. He later tried his hand at a number of ventures, and made four largely unsuccessful trips to the Klondike, taking groceries and hoping to profit from the gold rush. (Full article...) -
Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley (UK: /ˈwʊlstənkrɑːft/; née Godwin; 30 August 1797 – 1 February 1851) was an English novelist who is best known for writing the Gothic novel Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus (1818), which is considered an early example of science fiction. She also edited and promoted the works of her husband, the Romantic poet and philosopher Percy Bysshe Shelley. Her father was the political philosopher William Godwin and her mother was the philosopher and women's rights advocate Mary Wollstonecraft.
Mary's mother died 11 days after giving birth to her. She was raised by her father, who provided her with a rich if informal education, encouraging her to adhere to his own anarchist political theories. When she was four, her father married a neighbour, Mary Jane Clairmont, with whom Mary came to have a troubled relationship. (Full article...) -
Jorge Mario Pedro Vargas Llosa, 1st Marquess of Vargas Llosa (born 28 March 1936), more commonly known as Mario Vargas Llosa (/ˌvɑːrɡəs ˈjoʊsə/, Spanish: [ˈmaɾjo ˈβaɾɣas ˈʎosa]), is a Peruvian novelist, journalist, essayist and former politician. Vargas Llosa is one of Latin America's most significant novelists and essayists and one of the leading writers of his generation. Some critics consider him to have had a larger international impact and worldwide audience than any other writer of the Latin American Boom. In 2010, he won the Nobel Prize in Literature, "for his cartography of structures of power and his trenchant images of the individual's resistance, revolt, and defeat." He also won the 1967 Rómulo Gallegos Prize, the 1986 Prince of Asturias Award, the 1994 Miguel de Cervantes Prize, the 1995 Jerusalem Prize, the 2012 Carlos Fuentes International Prize, and the 2018 Pablo Neruda Order of Artistic and Cultural Merit. In 2021, he was elected to the Académie française.
Vargas Llosa rose to international fame in the 1960s with novels such as The Time of the Hero (La ciudad y los perros, literally The City and the Dogs, 1963/1966), The Green House (La casa verde, 1965/1968), and the monumental Conversation in the Cathedral (Conversación en la catedral, 1969/1975). He writes, prolifically, across an array of literary genres, including literary criticism and journalism. His novels include comedies, murder mysteries, historical novels, and political thrillers. Several, such as Captain Pantoja and the Special Service (1973/1978) and Aunt Julia and the Scriptwriter (1977/1982), have been adapted as feature films. (Full article...) -
Natalie Clifford Barney (October 31, 1876 – February 2, 1972) was an American writer who hosted a literary salon at her home in Paris that brought together French and international writers. She influenced other authors through her salon and also with her poetry, plays, and epigrams, often thematically tied to her lesbianism and feminism.
Barney was born into a wealthy family. She was partly educated in France, and expressed a desire from a young age to live openly as a lesbian. She moved to France with her first romantic partner, Eva Palmer. Inspired by the work of Sappho, Barney began publishing love poems to women under her own name as early as 1900. Writing in both French and English, she supported feminism and pacifism. She opposed monogamy and had many overlapping long and short-term relationships, including on-and-off romances with poet Renée Vivien and courtesan Liane de Pougy and longer relationships with writer Élisabeth de Gramont and painter Romaine Brooks. (Full article...) -

Robert Marshall (January 2, 1901 – November 11, 1939) was an American forester, writer and wilderness activist who is best remembered as the person who spearheaded the 1935 founding of the Wilderness Society in the United States. Marshall developed a love for the outdoors as a young child. He was an avid hiker and climber who visited the Adirondack Mountains frequently during his youth, ultimately becoming one of the first Adirondack Forty-Sixers. He also traveled to the Brooks Range of the far northern Alaskan wilderness. He wrote numerous articles and books about his travels, including the bestselling 1933 book Arctic Village.
A scientist with a PhD in plant physiology, Marshall became independently wealthy after the death of his father in 1929. He had started his outdoor career in 1925 as forester with the U.S. Forest Service. He used his financial independence for expeditions to Alaska and other wilderness areas. Later he held two significant public appointed posts: chief of forestry in the Bureau of Indian Affairs, from 1933 to 1937, and head of recreation management in the Forest Service, from 1937 to 1939, both during the administration of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. During this period, he directed the promulgation of regulations to preserve large areas of roadless land that were under federal management. Many years after his death, some of those areas were permanently protected from development, exploitation, and mechanization with the passage of the Wilderness Act of 1964. (Full article...) -
Emily Elizabeth Dickinson (December 10, 1830 – May 15, 1886) was an American poet. Little-known during her life, she has since been regarded as one of the most important figures in American poetry. Dickinson was born in Amherst, Massachusetts, into a prominent family with strong ties to its community. After studying at the Amherst Academy for seven years in her youth, she briefly attended the Mount Holyoke Female Seminary before returning to her family's home in Amherst. Evidence suggests that Dickinson lived much of her life in isolation. Considered an eccentric by locals, she developed a penchant for white clothing and was known for her reluctance to greet guests or, later in life, even to leave her bedroom. Dickinson never married, and most of her friendships were based entirely upon correspondence.
Although Dickinson was a prolific writer, her only publications during her lifetime were 10 of her nearly 1,800 poems and one letter. The poems published then were usually edited significantly to fit conventional poetic rules. Her poems were unique for her era; they contain short lines, typically lack titles, and often use slant rhyme as well as unconventional capitalization and punctuation. Many of her poems deal with themes of death and immortality (two recurring topics in letters to her friends), aesthetics, society, nature, and spirituality. (Full article...) -
Honoré de Balzac (/ˈbælzæk/ BAL-zak, more commonly US: /ˈbɔːl-/ BAWL-, French: [ɔnɔʁe d(ə) balzak]; born Honoré Balzac; 20 May 1799 – 18 August 1850) was a French novelist and playwright. The novel sequence La Comédie humaine, which presents a panorama of post-Napoleonic French life, is generally viewed as his magnum opus.
Owing to his keen observation of detail and unfiltered representation of society, Balzac is regarded as one of the founders of realism in European literature. He is renowned for his multi-faceted characters; even his lesser characters are complex, morally ambiguous and fully human. Inanimate objects are imbued with character as well; the city of Paris, a backdrop for much of his writing, takes on many human qualities. His writing influenced many famous writers, including the novelists Émile Zola, Charles Dickens, Marcel Proust, Gustave Flaubert, and Henry James, and filmmakers François Truffaut and Jacques Rivette. Many of Balzac's works have been made into films and continue to inspire other writers. James called him "really the father of us all." (Full article...) -
Rachel Louise Carson (May 27, 1907 – April 14, 1964) was an American marine biologist, writer, and conservationist whose sea trilogy (1941–1955) and book Silent Spring (1962) are credited with advancing marine conservation and the global environmental movement.
Carson began her career as an aquatic biologist in the U.S. Bureau of Fisheries, and became a full-time nature writer in the 1950s. Her widely praised 1951 bestseller The Sea Around Us won her a U.S. National Book Award, recognition as a gifted writer and financial security. Its success prompted the republication of her first book, Under the Sea Wind (1941), in 1952, which was followed by The Edge of the Sea in 1955 — both were also bestsellers. This sea trilogy explores the whole of ocean life from the shores to the depths. (Full article...) -
Edgar Allan Poe (né Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, author, editor, and literary critic who is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is widely regarded as a central figure of Romanticism and Gothic fiction in the United States, and of American literature. Poe was one of the country's earliest practitioners of the short story, and is considered the inventor of the detective fiction genre, as well as a significant contributor to the emerging genre of science fiction. He is the first well-known American writer to earn a living through writing alone, resulting in a financially difficult life and career.
Poe was born in Boston, the second child of actors David and Elizabeth "Eliza" Poe. His father abandoned the family in 1810, and when his mother died the following year, Poe was taken in by John and Frances Allan of Richmond, Virginia. They never formally adopted him, but he was with them well into young adulthood. He attended the University of Virginia but left after a year due to lack of money. He quarreled with John Allan over the funds for his education, and his gambling debts. In 1827, having enlisted in the United States Army under an assumed name, he published his first collection, Tamerlane and Other Poems, credited only to "a Bostonian". Poe and Allan reached a temporary rapprochement after the death of Allan's wife in 1829. Poe later failed as an officer cadet at West Point, declared a firm wish to be a poet and writer, and parted ways with Allan. (Full article...)
Selected excerpt
A recitation of "O frondens", from Ordo Virtutum, an allegorical morality play, or liturgical drama, by Hildegard of Bingen
More Did you know
- ... that the John Steinbeck play adaptation Of Mice and Men debuted on Broadway while the novel of the same name was still on the best seller lists?
- ... that Samuel Taylor Coleridge's Eminent Characters series includes: a lawyer, a speaker, a Unitarian, a general, a rebel, a betrayer, a poet, an actress, a philosopher, a friend, a playwright and a lord?
- ... that The Insider, a roman à clef, was Prime Minister P V Narasimha Rao's first novel?
- ... that a possible source for the poem The Fox, the Wolf and the Husbandman, by the 15th-century Scottish poet Robert Henryson, was Aesop's Fables as published by William Caxton?
- ... that Maria Konopnicka's poem Rota became so popular it was seen as an unofficial anthem of Poland?
Selected illustration
-
Engraver: J. Cooper; Restoration: Adam Cuerden"Le Noir Faineant in the Hermit's Cell", an illustration from an 1886 edition of Sir Walter Scott's 1819 novel Ivanhoe. Here, we see Le Noir Faineant, or the Black Knight (Richard the Lionheart in disguise) with Friar Tuck. Scott was an early pioneer in the development of the modern novel, and largely created the genre of historical fiction by weaving together legends and characters into his own creations. Ivanhoe, the story of one of the remaining Saxon noble families at a time when the English nobility was overwhelmingly Norman, was greatly influential on the modern view of the English folk hero Robin Hood, and has inspired many adaptations around the world in theatre, opera, film, and television.
-
Artist: Unknown; Restoration: Lise BroerA scene from a late-16th century publication of Nezami Ganjavi's adaptation of the classical Persian story Layla and Majnun, which is based on the real story of Qays ibn al-Mulawwah, a young man from the northern Arabian Peninsula and his love Layla. There are two versions of the story, but in both, Majnun goes mad when her father prevents him from marrying her. In the depicted scene, the eponymous star-crossed lovers meet for the last time before their deaths. Both have fainted and Majnun's elderly messenger attempts to revive Layla while wild animals protect the pair from unwelcome intruders.
-
Painting: John BauerA watercolor illustration by John Bauer (1882–1918) titled "Still, Tuvstarr sits and gazes down into the water", which accompanied Helge Kjellin's fairy tale "The Tale of the Moose Hop and the Little Princess Cotton Grass" in the 1913 edition of Among Gnomes and Trolls. In this scene, Tuvstarr looks for her lost heart in a tarn, symbolizing innocence lost.
Born and raised in Jönköping, Sweden, Bauer moved to Stockholm at age 16 to study at the Royal Swedish Academy of Fine Arts. He painted and illustrated in a romantic nationalistic style, in part influenced by the Italian Renaissance and Sami cultures. Most of his works are watercolors or prints in monochrome or muted colours; he also produced oil paintings and frescos. -
Artist: Walter Crane; Restoration: Lise BroerAn illustration from an 1893 version of A Wonder-Book for Girls and Boys by Nathaniel Hawthorne, which recounted the tale of King Midas. In Greek mythology, Midas was given ability to turn everything he touched into gold by the god Bacchus. However, he soon discovered that he was unable to even eat. Bacchus told him to wash in the river Pactolus, and the power flowed in the river, which was supposedly the reason for why the river was so rich in gold in later years. In Hawthorne's version, Midas' touch even turned his daughter to gold (pictured here).
-
Illustration: John BauerThe Princess and the Trolls, by John Bauer (1882–1918), was painted as an illustration for "The Changeling", a short story by Helena Nyblom. A watercolour held by the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm, it was first published in the 1913 edition of the anthology Among Gnomes and Trolls. It shows the princess Bianca Maria between two trolls in a forest. Bauer's illustrations of fairy tales and children's stories made him a household name in his native Sweden, and shaped perceptions of many fairy tale characters.
-
Illustration credit: Henry Holiday; restored by Adam CuerdenThe Hunting of the Snark is a nonsense poem written by English writer Lewis Carroll between 1874 and 1876. The plot follows a crew of ten trying to hunt the Snark, which may turn out to be a highly dangerous Boojum. This original illustration by Henry Holiday accompanies the verse:
'"`UNIQ--poem-0000001D-QINU`"' -
Artist: Albert RobidaA typical 20th-century aerial rotating house, as drawn by Albert Robida. The drawing shows a dwelling structure in the scientific romance style elevated above rooftops and designed to revolve and adjust in various directions. An occupant in the lower right points to an airship with a fish-shaped balloon in the sky, while a woman rides a bucket elevator on the left. Meanwhile, children fly a kite from the balcony as a dog watches from its rooftop doghouse.
-
Illustration: William Edward Frank Britten; restoration: Adam CuerdenŒnone is a poem written by Alfred, Lord Tennyson, in 1829. Inspired by the Greek mythological figure Oenone, first wife of Paris of Troy, the poem is a dramatic monologue following the lead-up to the Trojan War and the war itself. This illustration, by William Edward Frank Britten, is accompanied by the lines "O mother Ida, many-fountain'd Ida, / Dear mother Ida, harken ere I die".
-
Artist: Francis S. Walker; Engraving: Brothers Dalziel
Restoration: Adam CuerdenHermann Vezin in the title role of Dan'l Druce, Blacksmith, an 1876 play by W. S. Gilbert. In the story, Druce begins as a miser and drunkard whose wife has left him. Two army deserters find shelter at his house, but they rob him and abandon a baby girl there. Many years later, Druce has become a blacksmith, and the two men return to try to claim the girl. The play was a success, running for about 100 performances and enjoying tours and several revivals. -
Illustration: W. E. F. Britten; restoration: Adam Cuerden"The Sleeping Beauty" is a poem written by Alfred, Lord Tennyson, and published in 1830; it was later expanded and published in 1842 as "The Day-Dream". Based on the fairy tale Sleeping Beauty, the poem (as with many of Tennyson's adaptations of existing literary works) focuses on a single aspect of the story, the appearance of the eponymous character as she sleeps.
This illustration by W. E. F. Britten was published in 1901 to accompany a reprinting of "The Sleeping Beauty". It accompanies the poem's final lines: "She sleeps, nor dreams, but ever dwells / A perfect form in perfect rest." -
Illustration credit: Henry Holiday, after Lewis Carroll; restored by Adam CuerdenThe Hunting of the Snark is a poem composed by the English writer Lewis Carroll between 1874 and 1876, typically characterised as a nonsense poem. The plot follows a crew of ten who cross the ocean to hunt the Snark, which may turn out to be a highly dangerous Boojum. This is the second of Henry Holiday's original illustrations for the first edition of the poem. It introduces some of the crew, whose names all start with "B"; the Bellman and Baker are on the upper deck, with the Barrister seated in the background; below are the Billiard-marker, the Banker and the Broker, with the maker of Bonnets and Hoods visible behind.
-
The Quarrel of Oberon and Titania is an oil painting on canvas by the Scottish artist Joseph Noel Paton. Painted in 1849, it depicts the scene from William Shakespeare's comedy play A Midsummer Night's Dream, in which the fairy queen Titania and fairy king Oberon quarrel. When exhibited in Edinburgh in 1850, it was declared the "painting of the season". The painting was acquired by the National Galleries of Scotland in 1897, having initially been bought by the Royal Association for Promoting the Fine Arts.
-
Restoration: Adam CuerdenAn engraving by Gustave Doré of a scene from Miguel de Cervantes's Don Quixote, the most influential work of literature from the Spanish Golden Age in the Spanish literary canon. The scene illustrated here occurs early in the novel, when Alonso Quixano (Quixote's real name) has become obsessed with books of chivalry, and believes their every word to be true, despite the fact that many of the events in them are clearly impossible. Don Quixote was published in two separate volumes, ten years apart. It is considered a founding work of modern Western literature, and it regularly appears high on lists of the greatest works of fiction ever published.
-
Illustration: William BlakeThe Song of Los is an epic poem by William Blake first published in 1795 and considered part of his prophetic books. The poem consists of two sections, "Africa" and "Asia": in the first section Blake catalogues the decline of morality in Europe, which he blames on both the African slave trade and enlightenment philosophers, whereas in the second section he describes a worldwide revolution, urged by the eponymous Los.
The illustration here is from the book's frontispiece and shows Urizen presiding over the decline of morality. -
Illustration: Unknown; restoration: Adam CuerdenJeeves is a fictional character in a series of comedic short stories and novels by English author P. G. Wodehouse, in which he is depicted as the highly competent valet of a wealthy and idle young Londoner named Bertie Wooster. First appearing in the short story "Extricating Young Gussie" in 1915, Jeeves continued to feature in Wodehouse's work until his last completed novel, Aunts Aren't Gentlemen (1974). He also appeared in numerous films and television series, portrayed by such actors as Arthur Treacher, Michael Aldridge, and Dennis Price. The name and character of Jeeves have come to be identified with the quintessential valet or butler.
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that the 1985 manga series Tomoi contains the first depiction of HIV/AIDS in any literary medium in Japan?
- ... that Polish Renaissance poet Jan Kochanowski – considered "the founding father of Polish literature" – wrote threnodies, the first Polish-language tragedy, and epigrams?
- ... that a 1955 satirical comedy play by Kasymaly Jantöshev was one of the first signs of the relaxation of Soviet literary restrictions after the death of Joseph Stalin?
- ... that the biography of Karin Boye, written by Swedish literary critic Margit Abenius, was criticised for the conservative analysis of Boye's homosexuality?
- ... that History of the Mission of the Evangelical Brothers in the Caribbean by C. G. A. Oldendorp was the first book to publish Igbo-language terms in 1777?
- ... that campaign literature in the 1894 Montana capital referendum accused Helena residents of copious Manhattan consumption?
Today in literature
- 1906 - Arturo Uslar Pietri, Venezuelan writer born
- 1910 - Olga Berggolts, Russian poet born
- 1912 - Studs Terkel, American writer born
- 1917 - Juan Rulfo, Mexican novelist born
- 1929 - Adrienne Rich, American writer born
- 1984 - Irwin Shaw, American author died
Topics
| Literature: | History of literature · History of the book · Literary criticism · Literary theory · Publishing |
| By genre: | Biography · Comedy · Drama · Epic · Erotic · Fable · Fantasy · Historical fiction · Horror · Mystery · Narrative nonfiction · Nonsense · Lyric · Mythopoeia · Poetry · Romance · Satire · Science fiction · Tragedy · Tragicomedy · more... |
| By region: | African literature · Asian · European · Latin American · North American · Oceanic |
| By era: | Ancient literature · Early medieval · Medieval · Renaissance · Early Modern · Modern |
| By century: | 10th century in literature · 11th · 12th · 13th · 14th · 15th · 16th · 17th · 18th · 19th · 20th · 21st |
| Recent: | 2018 in literature· 2017 · 2016 · 2015 · 2014 · 2013 · 2012 · 2011 · 2010 · 2009 · 2008 · 2007 · more... |
Categories
Related portals
| Concepts: | |
| Genres: | |
| Religions: |
Things you can do
Related WikiProjects
WikiProjects related to literature:
| Concepts: | Biographies · Books · Comics · Magazines · Manga · Novels · Poetry · Short stories · Translation studies |
| Genres: | Alternate history · Children's literature · Crime · Fantasy · Horror · Mythology · Romance · Science fiction |
| Authors: | Honoré de Balzac · Roald Dahl · William Shakespeare |
| Series: | Artemis Fowl · Chronicles of Narnia · Discworld · Harry Potter · His Dark Materials · Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy · Inheritance Cycle · James Bond · King Arthur · Middle-earth · Percy Jackson · Redwall · A Series of Unfortunate Events · Shannara · Sherlock Holmes · A Song of Ice and Fire · Star Wars · Sword of Truth · Twilight · Warriors · Water Margin · Wizard of Oz |
| Regions: | Australian literature · Indian literature · Persian literature |
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus