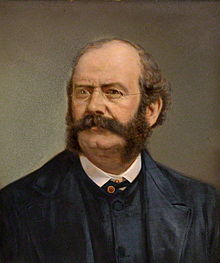Portal:Architecture
The Architecture Portal

Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings or other structures. The term comes from Latin architectura; from Ancient Greek ἀρχιτέκτων (arkhitéktōn) 'architect'; from ἀρχι- (arkhi-) 'chief', and τέκτων (téktōn) 'creator'. Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural symbols and as works of art. Historical civilisations are often identified with their surviving architectural achievements.
Architecture began as rural, oral vernacular architecture that developed from trial and error to successful replication. Ancient urban architecture was preoccupied with building religious structures and buildings symbolizing the political power of rulers until Greek and Roman architecture shifted focus to civic virtues. Indian and Chinese architecture influenced forms all over Asia and Buddhist architecture in particular took diverse local flavors. During the Middle Ages, pan-European styles of Romanesque and Gothic cathedrals and abbeys emerged while the Renaissance favored Classical forms implemented by architects known by name. Later, the roles of architects and engineers became separated.
Modern architecture began after World War I as an avant-garde movement that sought to develop a completely new style appropriate for a new post-war social and economic order focused on meeting the needs of the middle and working classes. Emphasis was put on modern techniques, materials, and simplified geometric forms, paving the way for high-rise superstructures. Many architects became disillusioned with modernism which they perceived as ahistorical and anti-aesthetic, and postmodern and contemporary architecture developed. Over the years, the field of architectural construction has branched out to include everything from ship design to interior decorating. (Full article...)
-
Castell Coch (Welsh for 'Red Castle'; Welsh pronunciation: [ˈkas.tɛɬ koːχ]) is a 19th-century Gothic Revival castle built above the village of Tongwynlais in South Wales. The first castle on the site was built by the Normans after 1081 to protect the newly conquered town of Cardiff and control the route along the Taff Gorge. Abandoned shortly afterwards, the castle's earth motte was reused by Gilbert de Clare as the basis for a new stone fortification, which he built between 1267 and 1277 to control his freshly annexed Welsh lands. This castle may have been destroyed in the native Welsh rebellion of 1314. In 1760, the castle ruins were acquired by John Stuart, 3rd Earl of Bute, as part of a marriage settlement that brought the family vast estates in South Wales.
John Crichton-Stuart, 3rd Marquess of Bute, inherited the castle in 1848. One of Britain's wealthiest men, with interests in architecture and antiquarian studies, he employed the architect William Burges to rebuild the castle, "as a country residence for occasional occupation in the summer", using the medieval remains as a basis for the design. Burges rebuilt the outside of the castle between 1875 and 1879, before turning to the interior; he died in 1881 and the work was finished by Burges's remaining team in 1891. Bute reintroduced commercial viticulture into Britain, planting a vineyard just below the castle, and wine production continued until the First World War. He made little use of his new retreat, and in 1950 his grandson, the 5th Marquess of Bute, placed it into the care of the state. It is now controlled by the Welsh heritage agency Cadw. (Full article...) -
Monnow Bridge (Welsh: Pont Trefynwy Welsh pronunciation: [pɔnt tre:vənʊɨ]), in Monmouth, Wales, is the only remaining fortified river bridge in Great Britain with its gate tower standing on the bridge. Such bridge towers were common across Europe from medieval times, but many were destroyed due to urban expansion, diminishing defensive requirements and the increasing demands of traffic and trade. The historical and architectural importance of the bridge and its rarity are reflected in its status as a scheduled monument and a Grade I listed building. The bridge crosses the River Monnow (Afon Mynwy) 500 metres (1,600 ft) above its confluence with the River Wye.
Monmouth had been a significant border settlement since the Roman occupation of Britain, when it was the site of the fort of Blestium. The River Wye may have been bridged at this time but the Monnow, being easily fordable, appears not to have had a crossing until after the Norman Conquest. According to the local tradition, construction of Monnow Bridge began in 1272 to replace a 12th-century Norman timber bridge. Through the medieval era, the English Civil War, and the Chartist uprising, the bridge played a significant, if ineffectual, role in defending Monmouth. It also served as a gaol, a munitions store, a lodge, an advertising hoarding, a focus for celebrations and, most significantly, as a toll gate. Much of the medieval development of Monmouth was funded by the taxes and tolls the borough was entitled to raise through royal charter. The tolls were collected through control of the points of entry to the town, including the gatehouse on Monnow Bridge. (Full article...) -

Queen's Gate House, still commonly known by its previous name of Baden-Powell House, is a conference centre in South Kensington, London. It was built as a tribute to Lord Baden-Powell, the founder of Scouting, and has served as the headquarters for The Scout Association, as a hostel providing modern and affordable lodging for Scouts, Guides, their families and the general public staying in London and as a conference and event venue.
The building committee, chaired by Sir Harold Gillett, Lord Mayor of London, purchased the site in 1956, and assigned Ralph Tubbs to design the house in the modern architectural style. The foundation stone was laid in 1959 by World Chief Guide Olave, Lady Baden-Powell, and it was opened in 1961 by Queen Elizabeth II. The largest part of the £400,000 cost was provided by the Scout Movement itself and the building previously included a number of tributes to the founder including hosting a small exhibition about Scouting, and a granite statue of Baden-Powell by Don Potter located outside the building. (Full article...) -
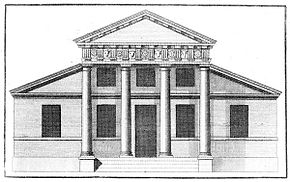
A villa with a superimposed portico, from Book IV of Palladio's I quattro libri dell'architettura, in an English translation published in London, 1736
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and the principles of formal classical architecture from ancient Greek and Roman traditions. In the 17th and 18th centuries, Palladio's interpretation of this classical architecture developed into the style known as Palladianism.
Palladianism emerged in England in the early 17th century, led by Inigo Jones, whose Queen's House at Greenwich has been described as the first English Palladian building. Its development faltered at the onset of the English Civil War. After the Stuart Restoration, the architectural landscape was dominated by the more flamboyant English Baroque. Palladianism returned to fashion after a reaction against the Baroque in the early 18th century, fuelled by the publication of a number of architectural books, including Palladio's own I quattro libri dell'architettura (The Four Books of Architecture) and Colen Campbell's Vitruvius Britannicus. Campbell's book included illustrations of Wanstead House, a building he designed on the outskirts of London and one of the largest and most influential of the early neo-Palladian houses. The movement's resurgence was championed by Richard Boyle, 3rd Earl of Burlington, whose buildings for himself, such as Chiswick House and Burlington House, became celebrated. Burlington sponsored the career of the artist, architect and landscaper William Kent, and their joint creation, Holkham Hall in Norfolk, has been described as "the most splendid Palladian house in England". By the middle of the century Palladianism had become almost the national architectural style, epitomised by Kent's Horse Guards at the centre of the nation's capital. (Full article...) -

Nuffield College, facing New Road, with the library tower topped by a flèche. The main entrance to the college is in the middle of the building to the left of the tower.
The buildings of Nuffield College, one of the colleges of the University of Oxford, are to the west of the city centre of Oxford, England, and stand on the site of the basin of the Oxford Canal. Nuffield College was founded in 1937 after a donation to the University by the car manufacturer Lord Nuffield; he gave land for the college, as well as £900,000 (approximately £246 million in present-day terms) to build and endow it. The architect Austen Harrison, who had worked in Greece and Palestine, was appointed by the University to design the buildings. His initial design, heavily influenced by Mediterranean architecture, was rejected by Nuffield, who called it "un-English" and refused to allow his name to be associated with it. Harrison reworked the plans, aiming for "something on the lines of Cotswold domestic architecture", as Nuffield wanted.
Construction of the second design began in 1949 and was finished in 1960. Progress was hampered by post-war building restrictions, and the effects of inflation on Nuffield's donation led to various cost-saving changes to the plans. In one change, the tower, which had been planned to be ornamental, was redesigned to hold the college's library. It was the first tower built in Oxford for 200 years and is about 150 feet (46 m) tall, including the flèche on top. The buildings are arranged around two quadrangles, with residential accommodation for students and fellows in one, and the hall, library and administrative offices in the other. The chapel has stained glass windows designed by John Piper. (Full article...) -
The construction of the first World Trade Center complex in New York City was conceived as an urban renewal project to help revitalize Lower Manhattan spearheaded by David Rockefeller. The project was developed by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey. The idea for the World Trade Center arose after World War II as a way to supplement existing avenues of international commerce in the United States.
The World Trade Center was originally planned to be built on the east side of Lower Manhattan, but the New Jersey and New York state governments, which oversee the Port Authority, could not agree on this location. After extensive negotiations, the New Jersey and New York state governments agreed to support the World Trade Center project, which was built at the site of Radio Row in the Lower West Side of Manhattan, New York City. To make the agreement acceptable to New Jersey, the Port Authority agreed to take over the bankrupt Hudson & Manhattan Railroad, which brought commuters from New Jersey to the Lower Manhattan site and, upon the Port Authority's takeover of the railroad, was renamed PATH. (Full article...) -

Profile of a Hoysala temple at Somanathapura
Hoysala architecture is the building style in Hindu temple architecture developed under the rule of the Hoysala Empire between the 11th and 14th centuries, in the region known today as Karnataka, a state of India. Hoysala influence was at its peak in the 13th century, when it dominated the Southern Deccan Plateau region. Large and small temples built during this era remain as examples of the Hoysala architectural style, including the Chennakesava Temple at Belur, the Hoysaleswara Temple at Halebidu, and the Kesava Temple at Somanathapura. These three temples were accorded UNESCO world heritage site status in 2023. Other examples of Hoysala craftsmanship are the temples at Belavadi, Amruthapura, Hosaholalu, Mosale, Arasikere, Basaralu, Kikkeri and Nuggehalli. Study of the Hoysala architectural style has revealed a negligible Indo-Aryan influence while the impact of Southern Indian style is more distinct.
Temples built prior to Hoysala independence in the mid-12th century reflect significant Western Chalukya influences, while later temples retain some features salient to Western Chalukya architecture but have additional inventive decoration and ornamentation, features unique to Hoysala artisans. Some three hundred temples are known to survive in present-day Karnataka state and many more are mentioned in inscriptions, though only about seventy have been documented. The greatest concentration of these are in the Malnad (hill) districts, the native home of the Hoysala kings. (Full article...) -
The Chicago Board of Trade Building is a 44-story, 604-foot (184 m) Art Deco skyscraper located in the Chicago Loop, standing at the foot of the LaSalle Street canyon. Built in 1930 for the Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT), it has served as the primary trading venue of the CBOT and later the CME Group, formed in 2007 by the merger of the CBOT and the Chicago Mercantile Exchange. In 2012, the CME Group sold the CBOT Building to a consortium of real estate investors, including GlenStar Properties LLC and USAA Real Estate Company.
The CBOT has been located at the site since 1885. A building designed by William W. Boyington stood at the location from 1885 to 1929, being the tallest building in Chicago from its construction until its clock tower was removed in 1895. The Boyington building became unsound in the 1920s and was demolished in 1929, replaced by the current building designed by Holabird & Root. The current building was itself Chicago's tallest until 1965, when it was surpassed by the Richard J. Daley Center. (Full article...) -

Holkham Hall. The severely Palladian south facade with its Ionic portico is devoid of arms or motif; not even a blind window is allowed to break the void between the windows and roof-line, while the lower windows are mere piercings in the stark brickwork. The only hint of ornamentation is from the two terminating Venetian windows.
Holkham Hall (/ˈhoʊkəm/ or /ˈhɒlkəm/) is an 18th-century country house near the village of Holkham, Norfolk, England, constructed in the Neo-Palladian style for the 1st Earl of Leicester (of the fifth creation of the title) by the architect William Kent, aided by Lord Burlington.
Holkham Hall is one of England's finest examples of the Palladian revival style of architecture, and the severity of its design is closer to Palladio's ideals than many of the other numerous Palladian style houses of the period. The Holkham Estate was built up by Sir Edward Coke, the founder of his family's fortune. He bought Neales manor in 1609, though never lived there, and made many other purchases of land in Norfolk to endow to his six sons. His fourth son, John, inherited the land and married heiress Meriel Wheatley in 1612. They made Hill Hall their home, and by 1659, John had complete ownership of all three Holkham manors. It is the ancestral home of the Coke family, who became Earls of Leicester. (Full article...) -
St. Michael's Golden-Domed Monastery (Ukrainian: Михайлівський золотоверхий монастир, romanized: Mykhailivskyi zolotoverkhyi monastyr) is a monastery in Kyiv, the capital of Ukraine, dedicated to Saint Michael the Archangel. It is located on the edge of the bank of the Dnipro river, to the northeast of the St Sophia Cathedral. The site is in the historical administrative neighbourhood of Uppertown and overlooks Podil, the city's historical commercial and merchant quarter. The monastery has been the headquarters of the Orthodox Church of Ukraine since December 2018.
Built in the Middle Ages by the Kievan Rus' ruler Sviatopolk II Iziaslavych, the monastery comprises the cathedral church, the Refectory Church of the Holy Apostle and Evangelist John the Theologian, constructed in 1713, the Economic Gate, constructed in 1760, and the bell tower, which was added in the 1710s. The exterior of the structure was remodelled in the Ukrainian Baroque style during the 18th century; the interior retained its original Byzantine architecture. (Full article...) -
The Oregon State Capitol is the building housing the state legislature and the offices of the governor, secretary of state, and treasurer of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is located in the state capital, Salem. Constructed from 1936 to 1938 and expanded in 1977, the current building is the third to house the Oregon state government in Salem. The first two capitols in Salem were destroyed by fire, one in 1855 and the other in 1935.
New York architects Trowbridge & Livingston conceived the current structure's Art Deco stripped classical design in association with Francis Keally. Much of the interior and exterior is made of marble. The Oregon State Capitol was placed on the National Register of Historic Places on June 29, 1988. (Full article...) -
Angkor Wat (/ˌæŋkɔːr ˈwɒt/; Khmer: អង្គរវត្ត, "City/Capital of Temples") is a Hindu-Buddhist temple complex in Cambodia. Located on a site measuring 162.6 hectares (1,626,000 m2; 402 acres) within the ancient Khmer capital city of Angkor, it is considered as the largest religious structure in the world by Guinness World Records. Originally constructed as a Hindu temple dedicated to the deity Vishnu, it was gradually transformed into a Buddhist temple towards the end of the century.
Angkor Wat was built at the behest of the Khmer king Suryavarman II in the early 12th century in Yaśodharapura (present-day Angkor), the capital of the Khmer Empire, as his state temple and eventual mausoleum. Angkor Wat combines two basic plans of Khmer temple architecture: the temple-mountain and the later galleried temple. It is designed to represent Mount Meru, home of the devas in Hindu mythology and is surrounded by a moat more than 5 km (3.1 mi). Enclosed within an outer wall 3.6 kilometres (2.2 mi) long are three rectangular galleries, each raised above the next. At the centre of the temple stands a quincunx of towers. Unlike most Angkorian temples, Angkor Wat is oriented to the west with scholars divided as to the significance of this. (Full article...) -
The Scottish Parliament Building (Scottish Gaelic: Pàrlamaid na h-Alba; Scots: Scots Pairlament Biggin) is the home of the Scottish Parliament at Holyrood, within the UNESCO World Heritage Site in central Edinburgh. Construction of the building commenced in June 1999 and the Members of the Scottish Parliament (MSPs) held their first debate in the new building on 7 September 2004. The formal opening by Queen Elizabeth II took place on 9 October 2004. Enric Miralles, the Catalan architect who designed the building, died before its completion.
From 1999 until the opening of the new building in 2004, committee rooms and the debating chamber of the Scottish Parliament were housed in the General Assembly Hall of the Church of Scotland located on The Mound in Edinburgh. Office and administrative accommodation in support of the Parliament were provided in buildings leased from the City of Edinburgh Council. The new Scottish Parliament Building brought together these different elements into one purpose-built parliamentary complex, housing 129 MSPs and more than 1,000 staff and civil servants. (Full article...) -

East range of First Quad
Oriel College (/ˈɔːriəl/) is a constituent college of the University of Oxford in Oxford, England. Located in Oriel Square, the college has the distinction of being the oldest royal foundation in Oxford (a title formerly claimed by University College, whose claim of being founded by King Alfred is no longer promoted). In recognition of this royal connection, the college has also been historically known as King's College and King's Hall. The reigning monarch of the United Kingdom (since 2022, Charles III) is the official visitor of the college.
The original medieval foundation established in 1324 by Adam de Brome, under the patronage of King Edward II of England, was the House of the Blessed Mary at Oxford, and the college received a royal charter in 1326. In 1329, an additional royal grant of a manor house, La Oriole, eventually gave rise to its common name. The first design allowed for a provost and ten fellows, called "scholars", and the college remained a small body of graduate fellows until the 16th century, when it started to admit undergraduates. During the English Civil War, Oriel played host to high-ranking members of the king's Oxford Parliament. (Full article...) -
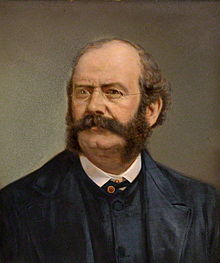
William Burges ARA (/ˈbɜːdʒɛs/; 2 December 1827 – 20 April 1881) was an English architect and designer. Among the greatest of the Victorian art-architects, he sought in his work to escape from both nineteenth-century industrialisation and the Neoclassical architectural style and re-establish the architectural and social values of a utopian medieval England. Burges stands within the tradition of the Gothic Revival, his works echoing those of the Pre-Raphaelites and heralding those of the Arts and Crafts movement.
Burges's career was short but illustrious; he won his first major commission for Saint Fin Barre's Cathedral in Cork in 1863 when he was 35. He died in 1881 at his Kensington home, The Tower House aged only 53. His architectural output was small but varied. Working with a long-standing team of craftsmen, he built churches, a cathedral, a warehouse, a university, a school, houses and castles. (Full article...)
Selected article –
30 Rockefeller Plaza (officially the Comcast Building; formerly RCA Building and GE Building) is a skyscraper that forms the centerpiece of Rockefeller Center in the Midtown Manhattan neighborhood of New York City, United States. Completed in 1933, the 66-story, 850 ft (260 m) building was designed in the Art Deco style by Raymond Hood, Rockefeller Center's lead architect. 30 Rockefeller Plaza was known for its main tenant, the Radio Corporation of America (RCA), from its opening in 1933 until 1988 and then for General Electric until 2015, when it was renamed for its current owner, Comcast. The building also houses the headquarters and New York studios of television network NBC; the headquarters is sometimes called 30 Rock, a nickname that inspired the NBC sitcom of the same name. The tallest structure in Rockefeller Center, the building is the 28th tallest in New York City and the 65th tallest in the United States, and was the third tallest building in the world when it opened.
30 Rockefeller Plaza's massing consists of three parts: the main 66-story tower to the east, a windowless section at the center, and a 16-story annex to the west. Though the building was designed to conform with the 1916 Zoning Resolution, it rises mostly as a slab, with setbacks mostly for aesthetic value. The facade is made of limestone, with granite at the base, as well as about 6,000 windows separated by aluminum spandrels. In addition to its offices and studios, 30 Rockefeller Plaza contains the Rainbow Room restaurant and an observation deck called Top of the Rock. 30 Rockefeller Plaza also includes numerous artworks and formerly contained the mural Man at the Crossroads by Diego Rivera. The entire Rockefeller Center complex is a New York City designated landmark and a National Historic Landmark, and parts of 30 Rockefeller Plaza's interior are also New York City landmarks. (Full article...)-
At 111 metres (364 ft), St Paul's Cathedral was the tallest building in London from 1710 until it was eventually surpassed by the 118 metre (387 ft) Millbank Tower in 1963. This in turn was overtaken by the BT Tower at 177 metres (581 ft) tall in 1964. Throughout the 1960s and 1970s several high-rise buildings were built, mostly in the western side of Central London and the City of London. In 1980, the 183 metre (600 ft) NatWest Tower (now Tower 42) was completed in the City of London. In 1991, One Canada Square was topped-out at 235 metres (771 ft), becoming the centrepiece of the Canary Wharf development.
The 2000s saw the beginnings of a boom in skyscraper building, mostly in the City of London and Canary Wharf. Since 2012, the tallest building in London has been The Shard at London Bridge, which was topped out at 309.6 metres (1,016 ft). There are several tall buildings planned for the City and Canary Wharf, with further clusters emerging in other districts of London including: Stratford, the South Bank, Elephant and Castle, Vauxhall, Nine Elms, Islington, Lewisham as well as in places in Outer London such as Croydon. (Full article...) -

The skyline of Lujiazui CBD in Pudong District with Oriental Pearl Tower, Shanghai International Finance Center, Jin Mao Tower, Shanghai World Financial Center and Shanghai Tower
The city of Shanghai, China is one of the fastest-growing cities in the world in terms of skyscraper construction, with the City of Shanghai reporting at the end of 2004 that there had been 6,704 buildings of 11 stories or more completed since 1990. In 2011 there are over 20,000 buildings 11 stories or higher and more than 1,000 buildings exceeding 30 stories in Shanghai. As of January 2019, there are 165 high-rise buildings either under construction, approved for construction, or proposed for construction, of which five are over 300 m (980 ft) high.
Shanghai's first building boom occurred in the 1920s and 1930s, during the city's heyday as a multinational center of business and finance. The city's international concessions permitted foreign investment, and with it came architectural styles from the West, as seen today in areas such as the French Concession and the Bund. After the Communist takeover in 1949 the city's development was stifled, punished for its earlier capitalist excesses. After economic reforms beginning in the 1980s, the city is undergoing its second construction boom to fulfill its desire to regain its status as an important global financial center. (Full article...) -

The Strat tower is the tallest observation tower in the United States
The city of Las Vegas, Nevada and its surrounding unincorporated communities in the Las Vegas Valley are the sites of more than 160 high-rises, 42 of which stand taller than 400 feet (122 m). The tallest structure in the city is the Strat tower, which rises 1,149 feet (350 m) just north of the Las Vegas Strip. The tower is also the tallest observation tower in the United States. However, the Strat is not considered a building because the vast majority of the tower is not habitable. The tallest building in Las Vegas is the Fontainebleau Las Vegas, which rises 735 feet (224 m) and was topped out in November 2008. This building remained unfinished for several years due to the late-2000s recession and opened in December 2023. The second tallest habitable building in the city is the 59-story Resorts World, which rises 673 feet (205 m) and was completed in 2021.
Beginning in the 1960s, high-rise hotels began to become more concentrated on the Las Vegas Strip. The first high-rise hotel and casino resort to rise higher than 492 feet (150 m) was the 529-foot (161 m) New York-New York Hotel & Casino, completed in 1997. Las Vegas entered into a skyscraper-building boom in the late 1990s that has continued to the present; of the city's 40 tallest skyscrapers, 39 were completed after 1997. As of 2012, the skyline of Las Vegas is ranked 66th in the world and 18th in the United States with 176 completed high-rises. (Full article...) -

Charles Holden by Benjamin Nelson, 1910
Charles Holden (12 May 1875 – 1 May 1960) was an English architect best known for designing many London Underground stations during the 1920s and 1930s. Other notable designs were Bristol Central Library, the Underground Electric Railways Company of London's headquarters at 55 Broadway and the University of London's Senate House. Many of his buildings have been granted listed building status, indicating that they are considered to be of architectural or historical interest and protecting them from unapproved alteration. He also designed over 60 war cemeteries and two memorials in Belgium and northern France for the Imperial War Graves Commission from 1920 to 1928.
Holden's early architectural training was in Bolton and Manchester where he worked for architects Everard W. Leeson and Jonathan Simpson before moving to London. After a short period with Arts and Crafts designer Charles Robert Ashbee, he went to work for Henry Percy Adams in 1899. He became Adams' partner in the firm in 1907 and remained with it for the rest of his career. (Full article...) -

Bunker Hill in Downtown Los Angeles
The tallest building in Los Angeles, California is the Wilshire Grand Center, which is 1,100 feet (335.3 m) tall and became the city's tallest building in 2017. It is also the tallest building in the state, the tallest building in the U.S. west of the Mississippi River, as well as the 15th-tallest building in the U.S. overall. Six of the ten tallest buildings in California are located in Los Angeles.
The 73-story U.S. Bank Tower, which rises 1,018 feet (310 m) in Downtown Los Angeles and was completed in 1989, is now the second-tallest building in Los Angeles. (Full article...) -
The Pritzker Architecture Prize is an international architecture award presented annually "to honor a living architect or architects whose built work demonstrates a combination of those qualities of talent, vision and commitment which has produced consistent and significant contributions to humanity and the built environment through the art of architecture.” Founded in 1979 by Jay A. Pritzker and his wife Cindy, the award is funded by the Pritzker family and sponsored by the Hyatt Foundation. It is considered to be one of the world's premier architecture prizes, and is often referred to as the Nobel Prize of architecture. (Full article...)
-

Skyline of Cleveland at sunrise.
Cleveland, the second most populous city in the U.S. state of Ohio, has 142 completed high-rises, 36 of which stand taller than 250 feet (76 m). The tallest building in Cleveland is the 57-story Key Tower, which rises 947 feet (289 m) on Public Square. The tower has been the tallest building in Ohio since its completion, in 1991; it also was the tallest building in the United States between Chicago and New York City before the completion, in 2007, of the Comcast Center in Philadelphia. The Terminal Tower, 771 feet (235 m), is the second tallest building in Cleveland and Ohio; at the time of its completion, in 1927, the building was the tallest in the world outside New York City.
The history of skyscrapers in Cleveland began in 1889, with the construction of the Society for Savings Building, often called the first skyscraper in the city. Cleveland went through an early building boom in the late 1920s and the early 1930s, during which several high-rise buildings, including the Terminal Tower, were constructed. The city experienced a second, much larger building boom from the early 1970s to the early 1990s, during which it saw the construction of over 15 skyscrapers, including the Key Tower and 200 Public Square. Overall, the city is the site of three of the four Ohio skyscrapers that rise at least 656 feet (200 m) in height; Cincinnati has the other. In 2020, the skyline of Cleveland was 27th in the United States and 96th in the world, ranked by buildings at least 330 feet (100 m) tall, with 18. (Full article...) -

All Saints' Church, Daresbury,
listed at Grade II
Runcorn is an industrial town in the borough of Halton, Cheshire, England. This list contains the 27 buildings that are recorded in the National Heritage List for England as designated listed buildings in the part of the borough lying to the south of the River Mersey outside the urban area of Runcorn. The area covered includes the villages of Clifton, Daresbury, Preston Brook, Preston on the Hill, and Moore. Three of the buildings in the area are classified as Grade II*, and the others are at Grade II; there are no buildings in Grade I. In the United Kingdom, the term listed building refers to a building or other structure officially designated as being of special architectural, historical, or cultural significance. These buildings are in three grades: Grade I consists of buildings of outstanding architectural or historical interest; Grade II* includes particularly significant buildings of more than local interest; Grade II consists of buildings of special architectural or historical interest. Buildings in England are listed by the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport on recommendations provided by English Heritage, which also determines the grading.
Although the urban area of Runcorn grew rapidly during the Industrial Revolution, and again with the growth of the New Town during the 1960s and 1970s, the surrounding area, mainly to the west of the town, has experienced only a small growth in population. The villages are small and discrete, and are separated by farmland and woodland. The area covered by the list is crossed by roads, railways, and canals, with which some of the listed buildings are associated. The oldest of these are the canals: the Bridgewater Canal, the Trent and Mersey Canal, the Weaver Navigation and the Manchester Ship Canal. The railways consist of the West Coast Main Line – the section between Crewe and Warrington, and the branch to Liverpool – and the Chester-Manchester Line. The major roads are the M56 motorway and the A6 road, together with sections of the A533, the A557 and the A558 roads. (Full article...) -

Tokyo is the most populated of Japan's 47 prefectures. In Tokyo, there are 53 buildings and structures that stand taller than 187 metres (614 feet). The tallest structure in the prefecture is Tokyo Skytree, a lattice tower that rises 634 metres (2,080 feet), which was completed in 2012. It also stands as the tallest structure in Japan, the tallest tower in the world and the third-tallest freestanding structure in the world. The tallest building and third-tallest overall structure in Tokyo is the 325.2-metre-tall Azabudai Hills Mori JP Tower in the Azabudai Hills development, completed in 2023 and being Tokyo's only supertall skyscraper. The second-tallest building is the 265-metre-tall (869 ft) Toranomon Hills Station Tower in the Toranomon Hills complex, which was completed in 2023. The prefecture's third-tallest building is the Toranomon Hills Mori Tower, which rises 52 storeys and 255 metres (837 feet) in height. Overall, as of October 2023, of the 25 tallest buildings and structures in Japan, 17 are in Tokyo.
Skyscrapers are a relatively recent phenomenon in Japan. Due to aesthetic and engineering concerns, Japan's Building Standard Law set an absolute height limit of 31 metres until 1963, when the limit was abolished in favor of a floor area ratio limit. Following these changes in building regulations, the Kasumigaseki Building was constructed and completed in 1968. Double the height of Japan's previous tallest building—the 17-story Hotel New Otani Tokyo—the Kasumigaseki Building is regarded as Japan's first modern high-rise building, rising 36 stories and 156 metres (512 feet) in height. A booming post-war Japanese economy and the hosting of the 1964 Summer Olympics helped lead to a building boom in Tokyo during the 1960s and 1970s. Construction continued through the 1980s and 1990s as the Japanese asset price bubble rose and fell. Mainland Tokyo is divided into two sections: Western Tokyo and the special wards of Tokyo. All of the prefecture's tallest buildings are within the 23 special wards, which comprise the area formerly incorporated as Tokyo City. Nishi-Shinjuku, a district within Shinjuku, was the prefecture's first major skyscraper development area. Starting with the construction of the Keio Plaza Hotel in the 1971, the district is now home to 13 of Tokyo's 46 tallest skyscrapers. (Full article...) -

John Douglas in late middle age
John Douglas (1830–1911) was an English architect based in Chester, Cheshire. His designs included new churches, alterations to and restoration of existing churches, church furnishings, new houses and alterations to existing houses, and a variety of other buildings, including shops, banks, offices, schools, memorials and public buildings. His architectural styles were eclectic, but as he worked during the period of the Gothic Revival, much of his work incorporates elements of the English Gothic style. Douglas is probably best remembered for his incorporation of vernacular elements in his buildings, especially half-timbering. Of particular importance is Douglas' use of joinery and highly detailed wood carving.
Douglas was born in the Cheshire village of Sandiway and was articled to the Lancaster architect E. G. Paley, later becoming his chief assistant. He established an office in Chester in either 1855 or 1860, from where he practised throughout his career. Initially he ran the office himself but in 1884 he appointed his assistant, Daniel Porter Fordham, as a partner. When Fordham retired in 1897, he was succeeded by Charles Howard Minshull. In 1909 this partnership was dissolved and Douglas ran the office alone until his death in 1911. As his office was in Chester, most of his work on houses was in Cheshire and North Wales, although some was further afield, in Lancashire, Merseyside, Greater Manchester, Warwickshire, Herefordshire, Worcestershire, Derbyshire, Surrey, and Scotland. (Full article...) -

South Somerset shown within Somerset and England
South Somerset is a local government district in the English county of Somerset. The South Somerset district occupies an area of 370 square miles (958 km2), stretching from its borders with Devon and Dorset to the edge of the Somerset Levels. The district has a population of about 158,000, and has Yeovil as its administrative centre.
In the United Kingdom, the term listed building refers to a building or other structure officially designated as being of special architectural, historical or cultural significance; Grade I structures are those considered to be "buildings of exceptional interest". Listing was begun by a provision in the Town and Country Planning Act 1947. Once listed, severe restrictions are imposed on the modifications allowed to a building's structure or its fittings. In England, the authority for listing under the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990 rests with Historic England, a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport; local authorities have a responsibility to regulate and enforce the planning regulations. (Full article...) -

The skyline of Detroit in 2015
This list of tallest buildings in Detroit ranks skyscrapers and high rises in the U.S. city of Detroit, Michigan by height. The tallest skyscraper in Detroit is the 73-story Detroit Marriott at the Renaissance Center, which rises 727 feet (222 m) along Detroit's International Riverfront.[A] It is the tallest building in the state of Michigan, the 97th-tallest building in the United States, and the second tallest hotel building in the Western Hemisphere. Another famous skyscraper is Ally Detroit Center, which stands as the 2nd-tallest building in the city and the state.
Detroit's history of skyscrapers began in 1889, with completion of the historic 10-story Hammond Building—considered the city's first steel-framed skyscraper. It was followed by the Savings Bank Building in 1895, the Majestic Building in 1896, and the Union Trust Building in 1896. Detroit witnessed a massive building boom during the Roaring Twenties, resulting in the construction of many of the city's ornate skyscrapers, including the Penobscot, Guardian, Fisher, Buhl, Stott, and Broderick. (Full article...) -

Himeji Castle is the most visited castle in Japan and a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The Japanese Sengoku period from the mid-15th to early 17th century was a time of nearly continual military conflict. Powerful military lords known as daimyōs, such as Oda Nobunaga, Toyotomi Hideyoshi or Tokugawa Ieyasu, struggled to unify Japan. During the Sengoku period, because of constant warfare, many fortifications and castles were built. Archetypal Japanese castle construction is a product of the Momoyama period and early Edo period.
A new era of castle construction began when the daimyo Nobunaga built Azuchi Castle from 1576 to 1579. Earlier fortifications of the Kamakura and Muromachi periods were crude large-scale structures; Azuchi, however, with rich ornamentation and a keep rising seven stories high, became the prototype for castle construction of the period. The style of Azuchi Castle marked a shift in the function of the castles from a place that was merely a fortress and military garrison to a political, cultural and economic center. The newer style castles functioned as home to the daimyōs, his family, and his most loyal retainers. Because of the expense of building such a lavish structure, castles in the style of Azuchi, functioned also to highlight the power and prestige of the daimyōs. These new castles were built of wood and plaster on a stone foundation. Generally the main keep or tenshu was positioned at the highest point, surrounded by a series of interlocking baileys with walls, small towers and pathways. Residential buildings were located in one of the outer circles. The daimyō conducted his business in the citadel. (Full article...) -

Norman doorway in the undercroft of Norton Priory, built in local red sandstone
Runcorn is an industrial town in Halton, Cheshire, England, on the south bank of the River Mersey where it narrows at Runcorn Gap. In the town are the 61 buildings that are recorded in the National Heritage List for England as designated listed buildings in the current urban area of Runcorn, including the districts of Runcorn, Halton, Weston, Weston Point, and Norton. Two of these are classified as being in Grade I, nine in Grade II*, and 51 in Grade II.
In the United Kingdom, the term "listed building" refers to a building or other structure officially designated as being of special architectural, historical or cultural significance. These buildings are in three grades: Grade I consists of buildings of outstanding architectural or historical interest; Grade II* includes particularly significant buildings of more than local interest; Grade II consists of buildings of special architectural or historical interest. Buildings in England are listed by the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport on recommendations provided by English Heritage, which also determines the grading. (Full article...) -
West Somerset is a local government district in the English county of Somerset. In the United Kingdom, the term listed building refers to a building or other structure officially designated as being of special architectural, historical or cultural significance; Grade I structures are those considered to be "buildings of exceptional interest". Listing was begun by a provision in the Town and Country Planning Act 1947. Once listed, severe restrictions are imposed on the modifications allowed to a building's structure or its fittings. In England, the authority for listing under the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990 rests with Historic England, a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport; local authorities have a responsibility to regulate and enforce the planning regulations.
The district of West Somerset covers a largely rural area, with a population, according to the 2011 census, of 35,300 in an area of 740 square kilometres (290 sq mi). The largest centres of population are the coastal towns of Minehead and Watchet. The council's administrative headquarters are in the village of Williton. (Full article...)
-

Taipei 101 (Chinese: 台北101; pinyin: Táiběi 101; stylized in all caps), formerly known as the Taipei World Financial Center, is a skyscraper in Taipei, Taiwan. It is owned by Taipei Financial Center Corporation. The building was officially classified as the world's tallest from its opening on 31 December 2004 (in time to celebrate New Year's Eve). However, the Burj Khalifa surpassed Taipei 101 in 2010. Upon completion, it became the world's first skyscraper to exceed a height of half a kilometer (about 0.3 miles). As of 2023, Taipei 101 is the tallest building in Taiwan and the eleventh tallest building in the world.
The elevators of Taipei 101 that transport passengers from the 5th to the 89th floor in 37 seconds (attaining 60.6 km/h (37.7 mph)) set speed records. In 2011, Taipei 101 was awarded a Platinum certificate rating under the LEED certification system for energy efficiency and environmental design, becoming the tallest and largest green building in the world. The structure regularly appears as an icon of Taipei in international media, and the Taipei 101 fireworks displays are a regular feature of New Year's Eve broadcasts and celebrations. (Full article...) -
The Lafayette Park Historic District is located in central Albany, New York, United States. It includes the park and the combination of large government buildings and small rowhouses on the neighboring streets. In 1978 it was recognized as a historic district and listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP). Many of its contributing properties are themselves listed on the National Register. One of them, the New York State Capitol, is a National Historic Landmark as well. Other government buildings include City Hall, the building housing Albany County government, the state's highest court and the offices of its Education Department along with the offices of the City School District of Albany. The Episcopal Diocese of Albany's cathedral is at one corner of the district.
While the state capitol building has always been located on its present site, for most of the 19th century the neighborhood was best known for the townhouses on Elk Street, then one of the most desirable addresses in the city. Many politicians, including some of the state's governors and presidents Martin Van Buren and Franklin D. Roosevelt, lived there at different times. Henry James would recall the neighborhood from his childhood visits to his aunt as "vaguely portentous, like beasts of the forest not wholly exorcised." Two significant technological accomplishments—the development of the first working electromagnet and the construction of the first cantilevered arch bridge—also took place within it. Henry Hobson Richardson, Philip Hooker and Marcus T. Reynolds are among the architects with buildings in the district. (Full article...) -

The Millennium Stadium (Welsh: Stadiwm y Mileniwm), known since 2016 as the Principality Stadium (Welsh: Stadiwm Principality) for sponsorship reasons, is the national stadium of Wales. Located in Cardiff, it is the home of the Wales national rugby union team and has also held Wales national football team games. Initially built to host the 1999 Rugby World Cup and replacing the National Stadium, it has gone on to host many other large-scale events, such as the Tsunami Relief Cardiff concert, the Super Special Stage of Wales Rally Great Britain, the Speedway Grand Prix of Great Britain and various concerts. It also hosted FA Cup, League Cup and Football League play-off finals while Wembley Stadium was being redeveloped between 2001 and 2006, as well as football matches during the 2012 Summer Olympics.
The stadium is owned by Millennium Stadium plc, a subsidiary company of the Welsh Rugby Union (WRU). The architects were Bligh Lobb Sports Architecture. The structural engineers were WS Atkins and the building contractor was Laing. The total construction cost of the stadium was £121 million, of which the Millennium Commission funded £46 million. (Full article...) -
The Shamrock was a hotel constructed between 1946 and 1949 by wildcatter Glenn McCarthy southwest of downtown Houston, Texas next to the Texas Medical Center. It was the largest hotel built in the United States during the 1940s. The grand opening of the Shamrock is still cited as one of the biggest social events ever held in Houston. Sold to Hilton Hotels in 1955 and operated for over three decades as the Shamrock Hilton, the facility endured financial struggles throughout its history. In 1985, Hilton Hotels donated the building to the Texas Medical Center and the structure was demolished on June 1, 1987. (Full article...)
-
Churche's Mansion is a timber-framed, black-and-white Elizabethan mansion house at the eastern end of Hospital Street in Nantwich, Cheshire, England. The Grade I listed building dates from 1577, and is one of the very few to have survived the Great Fire of Nantwich in 1583.
Built for Richard Churche, a wealthy Nantwich merchant, and his wife, it remained in their family until the 20th century. In 1930, it was rescued from being shipped to the US by Edgar Myott and his wife, who began restoration work. As well as a dwelling, the mansion has been used as a school, restaurant, shop, and granary and hay store. (Full article...) -

The Liuhe Pagoda, or Six Harmonies Pagoda, in Hangzhou, 60 m (197 ft) in height, erected in 1156 and completed in 1165 AD
The architecture of the Song dynasty (960–1279) was noted for its towering Buddhist pagodas, enormous stone and wooden bridges, lavish tombs, and extravagant palaces. Although literary works on architecture existed beforehand, architectural writing blossomed during the Song dynasty, maturing into a more professional form that described dimensions and working materials in a concise, organized manner. In addition to the examples still standing, depictions in Song artwork, architectural drawings, and illustrations in published books all aid modern historians in understanding the architecture of the period.
The professions of architect, master craftsman, carpenter, and structural engineer did not have the high status of the Confucian scholar-officials during the dynastic era. Architectural knowledge had been passed down orally for thousands of years, usually from craftsman fathers to their sons. There were also government agencies and schools for construction, building, and engineering. The Song dynasty's building manuals aided not only the various private workshops, but also the craftsmen employed by the central government. (Full article...) -

Photochrom of the Chester Rows as seen from the Cross, 1895
Chester Rows are a set of structures in each of the four main streets of Chester, in the United Kingdom, consisting of a series of covered walkways on the first floor behind which are entrances to shops and other premises. At street level is another set of shops and other premises, many of which are entered by going down a few steps.
Dating from the medieval era, the Rows may have been built on top of rubble remaining from the ruins of Roman buildings, but their origin is still subject to speculation. In some places the continuity of the Rows has been blocked by enclosure or by new buildings, but in others modern buildings have retained the Rows in their designs. Undercrofts or "crypts" were constructed beneath the buildings in the Rows. The undercrofts are made from stone while most of the buildings in the Rows are timber. (Full article...) -
University Mall, originally The Mall, is a defunct shopping center in Little Rock, Arkansas, which operated for approximately 40 years, from 1967 until 2007. When it closed, University Mall was the oldest enclosed shopping center in the Little Rock metropolitan area. Located in the central part of Little Rock, the site is situated along South University Avenue, north of the University of Arkansas at Little Rock and Interstate 630. The mall was managed by Indianapolis-based Simon Property Group.
The Mall was initially a success, but its popularity declined as new retail outlets in Little Rock drew customers away. The departure of its anchor stores, beginning with the bankruptcy of Montgomery Ward in 2001, left more than half of the mall empty. Throughout the 1990s, the mall steadily declined as retailers and customers left. Due to the waning popularity and litigation involving the deterioration of the building, the mall was sold in 2007 to Strode Property Company, and the remaining few tenants were told to vacate. Demolition began for the primary structure in early 2008. Prior to this, associated buildings were razed beginning in December 2007, starting with the former Montgomery Ward auto center, as well as the former JCPenney auto center, which had been used several years as an automotive maintenance facility for the City of Little Rock. (Full article...) -
The Manila Hotel is a 550-room, historic five-star hotel located along Manila Bay in Manila, Philippines. The hotel is the oldest premiere hotel in the Philippines built in 1909 to rival Malacañang Palace, the official residence of the President of the Philippines and was opened on the commemoration of American Independence on July 4, 1912. The hotel complex was built on a reclaimed area of 35,000 square metres (380,000 sq ft) at the northwestern end of Rizal Park along Bonifacio Drive in Ermita. Its penthouse served as the residence of General Douglas MacArthur during his tenure as the Military Advisor of the Philippine Commonwealth from 1935 to 1941.
The hotel used to host the offices of several foreign news organizations, including The New York Times. It has hosted world leaders and celebrities, including authors Ernest Hemingway and James A. Michener; actors Douglas Fairbanks, Jr. and John Wayne; publisher Henry Luce; entertainers Sammy Davis, Jr., Michael Jackson and The Beatles; Charles, Prince of Wales (now King Charles III); and U.S. President Bill Clinton. (Full article...) -
Andriivskyi Descent or Andrew's Descent (Ukrainian: Андріївський узвіз, Andriivs′kyi uzviz) is a historic descent connecting Kyiv's Upper Town neighborhood and the historically commercial Podil neighborhood. The street, often advertised by tour guides and operators as the "Montmartre of Kyiv", is a major tourist attraction of the city. It is included in the list of national landmarks by the government resolution. In addition, the street is also part of the Kyiv city historic reserve "Ancient Kyiv", while the St. Andrew's Church belongs to the National historic reserve "Sophia of Kyiv".
The descent, 720 metres (2,360 ft) in length, is constructed of laid cobblestones and connects Old Kyiv (Upper city) with Podil (Lower city). It starts at the end of Volodymyrska Street and winds down steeply around the Zamkova Hora hill, ending near the Kontraktova Square. Andrew's Descent is marked by some historic landmarks, including the Castle of Richard the Lionheart, the 18th century baroque Saint Andrew's Church, famed Russian writer Mikhail Bulgakov's house, and numerous other monuments. (Full article...) -
Old St Paul's Cathedral was the cathedral of the City of London that, until the Great Fire of 1666, stood on the site of the present St Paul's Cathedral. Built from 1087 to 1314 and dedicated to Saint Paul, this building was perhaps the fourth such church at this site on Ludgate Hill, going back to the 7th century.
Work on the cathedral began after a fire in 1087, which destroyed the previous church. Work took more than 200 years, and over that time the architecture of the church changed from Norman Romanesque to early English Gothic. The church was consecrated in 1240, enlarged in 1256 and again in the early 14th century. At its completion in the mid-14th century, the cathedral was one of the longest churches in the world, had one of the tallest spires and some of the finest stained glass. (Full article...) -
Chana School is a Registered Historic Place in Ogle County, Illinois, in the county seat of Oregon, Illinois. One of six Oregon sites listed on the Register, the school is an oddly shaped, two-room schoolhouse which has been moved from its original location. Chana School joined the Register in 2005 as an education museum.
The schoolhouse was built in 1883, in the village of Chana, Illinois. Due to the elimination of the Chana School District, the school was abandoned by the 1960s. A restoration effort was undertaken in the late 1990s, ending with a move and refurbishment in 2002 and 2003. The building now stands in a public park along the Rock River in Oregon, Illinois. Its interior also features architectural elements which set it apart from the typical 19th-century schoolhouse. From a distance, the building is dominated by its bell tower. (Full article...) -
Fort Greble was an American Civil War-era Union fortification constructed as part of the defenses of Washington, D.C. during that war. Named for First Lieutenant John Trout Greble, the first West Point graduate killed in the U.S. Civil War, it protected the junction of the Anacostia and Potomac rivers, and from its position on a bluff in the Congress Heights, precluded any bombardment of the Washington Navy Yard and southeastern portions of the city. It was supported by Fort Carroll to the northeast and Fort Foote to the south. It never fired a shot during the war, and after a brief stint as a U.S. Army Signal Corps training facility, was abandoned and the land returned to its natural state. As of July 2007, the site of the fort is a community park. (Full article...)
-

Elgin Cathedral is a historic ruin in Elgin, Moray, north-east Scotland. The cathedral, dedicated to the Holy Trinity, was established in 1224 on land granted by King Alexander II outside the burgh of Elgin and close to the River Lossie. It replaced the cathedral at Spynie, 3 kilometres (2 mi) to the north, which was served by a small chapter of eight clerics. By 1226, the new and developing cathedral was staffed with 18 canons increasing to 23 by 1242. A damaging fire in 1270 prompted a significantly enlarged building. It remained unaffected by the Wars of Scottish Independence, but again suffered extensive fire damage in 1390 when attacked by Robert III's brother Alexander Stewart, Earl of Buchan, also known as the Wolf of Badenoch. In 1402, the cathedral precinct again suffered an incendiary attack by the Lord of the Isles followers.
As the cathedral grew, so did the number of clerics and craftsmen. The repairs following the 1270 and 1390 fires resulted in the doubling in length of the choir and the provision of outer aisles to both the nave and choir. Today, some parts of walls reach their full height while others are at foundation level, but the overall cruciform shape is still discernible. A mostly intact octagonal chapter house dates from the major enlargement after the fire of 1270. The gable wall above the double door entrance that links the west towers is nearly complete and was rebuilt after the fire of 1390. It accommodates a large window opening that now only contains stub tracery work and fragments of a large rose window. The transepts and the south aisle of the choir contain recessed and chest tombs with effigies of bishops and knights. The now grass-covered floor bears large flat slabs that mark the positions of early graves. The residences of the dignitaries, canons and chaplains that stood in the chanonry were also destroyed by the fires of 1270, 1390 and 1402 forming part of the reconstruction process. Only the precentor's manse is substantially intact, while two others have been incorporated into private buildings. Both west front towers are mostly complete and were part of the initial construction. A protective wall of massive proportions surrounded the cathedral precinct, but only two small sections have survived. The wall had four access gates but only one, the Pans Port, still exists. (Full article...) -
Beaumont House, occasionally known as Claremont, is an eclectic Romanesque-Classical brick residence located at 631 Glynburn Road in Beaumont, South Australia. Beaumont House was constructed for Augustus Short, the first Anglican bishop of Adelaide and founder of St Peter's Cathedral. It was constructed on land initially owned by Sir Samuel Davenport, a wealthy Adelaide landlord. Following Short's move back to England, Davenport purchased the house—the second of five eventual owners. Following three sales between 1907 and 1911, the house was then transferred to the National Trust of South Australia in 1968 and has been listed on the South Australian Heritage Register since 24 July 1980. (Full article...)
General images –
-
Chapel of the Holy Shroud, Turin (from Baroque architecture)
-
Beurs van Berlage in Amsterdam, 1903 (Hendrik Petrus Berlage) (from Traditionalist School (architecture))
-
The Church of St-Gervais-et-St-Protais, the first Paris church with a façade in the new Baroque style (1616–20) (from Baroque architecture)
-
The tower of the Helsinki Olympic Stadium (Y. Lindegren & T. Jäntti, built in 1934–38) (from Functionalism (architecture))
-
Basilica of Bom Jesus. A World Heritage Site built in Baroque style and completed in 1604 AD. It has the body of St. Francis Xavier. (from Baroque architecture)
-
The Mexico City Metropolitan Cathedral built from 1573 to 1813. (from Baroque architecture)
-
Interior of the Basilica and Convent of Nossa Senhora do Carmo, Recife, Brazil, built between 1665 and 1767 (from Baroque architecture)
-
In Ireland: Yola hut (from Architecture)
-
In adding the dome to the Florence Cathedral (Italy) in the early 15th century, the architect Filippo Brunelleschi not only transformed the building and the city, but also the role and status of the architect. (from Architecture)
-
Body plan of a ship showing the hull form (from Architecture)
-
Zlín in the Czech Republic (from Functionalism (architecture))
-
Corpus Christi Church, Grand Duchy of Lithuania (today Nyasvizh, Belarus), 1586 and 1593 (from Baroque architecture)
-
Typical railing, flat roof, stucco and colour detail in Nordic funkis (SOK warehouse and offices, 1938, Finland) (from Functionalism (architecture))
-
Church of Santa Engrácia, Lisbon (now National Pantheon of Portugal; begun 1681) (from Baroque architecture)
-
Façade of the Church of the Gesù Rome (consecrated 1584) (from Baroque architecture)
-
The dome of Les Invalides, Paris (from Baroque architecture)
-
Znamenskaya Church (Dubrovitsy) 1690-1698 Podolsk, Moscow (from Baroque architecture)
-
Church of Our Saviour, Copenhagen (1682–1747) (from Baroque architecture)
-
The Zwinger in Dresden by Matthäus Daniel Pöppelmann (1697–1716), reconstructed in the 1950s and 1960s, after the damage of World War II. (from Baroque architecture)
-
Plan of the second floor (attic storey) of the Hôtel de Brionne in Paris – 1734. (from Architecture)
-
Troja Palace, Prague (1679–1691) (from Baroque architecture)
-
Södra Ängby, 1938 (from Functionalism (architecture))
-
Interior view of dome of the Church of the Gesù by Giacomo Barozzi da Vignola, and Giacomo della Porta (from Baroque architecture)
-
Obchodný a obytný dom Luxor (Residential and Commercial House Luxor), 1937, in Bratislava (Slovakia) (from Functionalism (architecture))
-
Upper Belvedere Palace in Vienna (1721–23) (from Baroque architecture)
-
In Lesotho: rondavel stones (from Architecture)
-
In Norway: wood and elevated-level (from Architecture)
-
Charles Rennie Mackintosh – Music Room 1901 (from Architecture)
-
Saints Peter and Paul Church, Kraków, Poland by Giovanni Maria Bernardoni (1605–1619) (from Baroque architecture)
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that Ron Labinski has been described as the world's first sports-venue architect?
- ... that the architect of the Asakusa Culture Tourist Information Center thought of stacked nagaya houses while designing it?
- ... that the heritage-registered Weston House, designed by architect Cecil Wood for George Weston, was damaged in a series of earthquakes in Christchurch and later demolished?
- ... that confectioner William Westerfeld hired architect Henry Geilfuss to design his home in San Francisco, and then died in it?
- ... that the owner of 130 West 30th Street would have renamed the structure the "Beaver Pelt Building" if it could not be named after its architect?
- ... that landscape architect Harriet Pattison collaborated with her lover Louis Kahn on the design of Four Freedoms Park and the grounds of the Kimbell Art Museum?
Related portals
-
Waldorf Astoria New York by Joseph Pennell (1860–1926) (from Portal:Architecture/Travel images)
-
The Royal College of Music, London (from Portal:Architecture/Academia images)
-
Beirut, Lebanon, last third of the 19th century (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
Albert Memorial, London (from Portal:Architecture/Monument images)
-
Toda tribe hut, India (from Portal:Architecture/Ancient images)
-
Cleveland Tower at Princeton University (from Portal:Architecture/Academia images)
-
Flinders Street Station (1927), by Victoria State Transport Authority (from Portal:Architecture/Travel images)
-
Dunrobin Castle, Sutherland, Scotland (from Portal:Architecture/Castle images)
-
InterContinental Amstel Amsterdam (2009) in Amsterdam, Netherlands (from Portal:Architecture/Travel images)
-
Competition design for the Montana State Capitol by George R. Mann 1896 (from Portal:Architecture/Civic building images)
-
Sparrenburg Castle, Bielefeld, Germany (from Portal:Architecture/Castle images)
-
Grauman's Chinese Theatre, by Carol M. Highsmith (edited by Diliff) (from Portal:Architecture/Theatres and Concert hall images)
-
Arc de Triomphe, Paris (from Portal:Architecture/Monument images)
-
Ksiaz, Silesia, Poland (from Portal:Architecture/Castle images)
-
Canberra, Australia (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
Saint Isaac's Square, Saint Petersburg, Russia (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
De Zoeker windmill, Netherlands. (from Portal:Architecture/Industrial images)
-
Site and principle storey plan of the White House, Washington DC (from Portal:Architecture/Civic building images)
-
Treasury of the Athenians at Delphi, Greece (from Portal:Architecture/Ancient images)
-
Eiffel Tower, Paris (from Portal:Architecture/Monument images)
-
Melbourne Docklands panorama (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
Egeskov Castle, Denmark (from Portal:Architecture/Castle images)
-
Bodie, California, Ghost town (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
Cuzco, Peru (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
Mesoamerican step-pyramid nicknamed El Castillo at Chichen Itza (from Portal:Architecture/Ancient images)
-
Pitstone-windmill (from Portal:Architecture/Industrial images)
-
Radcliffe Camera, Oxford, England (from Portal:Architecture/Academia images)
-
Smithsonian Institution Building, Washington DC (from Portal:Architecture/Academia images)
-
Sydney Opera House, Australia (from Portal:Architecture/Theatres and Concert hall images)
-
New York panorama (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
Centre Block, Ottawa, Canada (from Portal:Architecture/Civic building images)
-
Panoramic view of Milwaukee 1890-1900 (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
Stockwell Bus Garage, London (from Portal:Architecture/Travel images)
-
Library of Congress, Washington DC (from Portal:Architecture/Academia images)
-
Manhattan from Staten Island Ferry (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
The castle of Maintenon. France (from Portal:Architecture/Castle images)
-
Bronx Community College Library, by Detroit Publishing Company (from Portal:Architecture/Academia images)
-
Amsterdam Centraal railway station (c. 1895) in Amsterdam, Netherlands (from Portal:Architecture/Travel images)
-
Taj Mahal, India (from Portal:Architecture/Monument images)
-
Ivan Vazov National Theatre in Sofia, Bulgaria (from Portal:Architecture/Theatres and Concert hall images)
-
Geodesic Radomes at Radome by Preston Keres, United States Navy (from Portal:Architecture/Industrial images)
-
Skyline of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
The State Library of Victoria's La Trobe Reading Room, Melbourne, Australia (from Portal:Architecture/Academia images)
-
Aqueduct of Segovia (from Portal:Architecture/Industrial images)
-
Walt Disney Concert Hall, Los Angeles (from Portal:Architecture/Theatres and Concert hall images)
-
Battenberg Mausoleum, Sofia (from Portal:Architecture/Monument images)
-
Eiffel Tower, Paris (from Portal:Architecture/Monument images)
-
Schloss Vaduz at Vaduz, by Michael Gredenberg (from Portal:Architecture/Castle images)
-
Quays Waterford, Ireland (c.1890-1900) (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
Stockholm Central Station, Sweden (from Portal:Architecture/Travel images)
-
United States Capitol, Washington DC (from Portal:Architecture/Civic building images)
-
Alatskivi Castle, Estonia (from Portal:Architecture/Castle images)
-
British Museum Reading Room, London (from Portal:Architecture/Academia images)
-
Library of Congress Main Reading Room, Washington DC (from Portal:Architecture/Academia images)
-
Curve, Leicester, UK (from Portal:Architecture/Theatres and Concert hall images)
-
Menier Chocolate factory in Noisiel (from Portal:Architecture/Industrial images)
-
Castle Neuschwanstein, Germany (from Portal:Architecture/Castle images)
-
The research room at the New York Public Library (from Portal:Architecture/Academia images)
-
Al-Ameen College of Pharmacy, Bangalore (from Portal:Architecture/Academia images)
-
Gyeonghoeru Pavilion at Gyeongbokgung (from Portal:Architecture/Palace images)
-
London King's Cross railway station departures concourse (from Portal:Architecture/Travel images)
-
Statue of Liberty, New York (from Portal:Architecture/Monument images)
-
Mespelbrunn Castle, Germany (from Portal:Architecture/Castle images)
-
Melbourne Skyline from Rialto tower, Australia (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
Grand Central Terminal, New York, NY (from Portal:Architecture/Travel images)
-
Grand Central Terminal, New York, NY (from Portal:Architecture/Travel images)
-
Aqueduct of Segovia, Spain (from Portal:Architecture/Ancient images)
-
Centennial Hall, Poland (from Portal:Architecture/Monument images)
-
Palau de les Arts Reina Sofía, Valencia, Spain. by Diliff (from Portal:Architecture/Theatres and Concert hall images)
-
John F. Kennedy Library, Boston (from Portal:Architecture/Academia images)
-
Panorama of St. Louis, Missouri (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
Chicago skyline (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
Chicago Theatre (from Portal:Architecture/Theatres and Concert hall images)
-
L'Hemisfèric — Imax Cinema, Planetarium and Laserium at the Ciutat de les Arts i les Ciències by Diliff (from Portal:Architecture/Theatres and Concert hall images)
-
Royal Avenue, Belfast, Ireland (c.1890-1900) (from Portal:Architecture/Townscape images)
-
British Columbia Parliament Buildings, Victoria, Canada (from Portal:Architecture/Civic building images)
Major topics
- Basic topics Architect • List of architects • Architecture • List of architecture firms • Style • List of buildings • New article announcements • more....
- Architectural history Timeline of architectural styles • Ancient Egyptian • Harappan • Inca • Mayan • Persian • Sumerian • Ancient Greek • Roman • Byzantine • Romanesque • Moorish • Gothic • Renaissance • Mannerism • Baroque • Ottoman • Palladian • Neoclassicism • Revival • Jugendstil • Art Deco • Modern • Postmodern • New Classical • more....
- Architectural theory Critical regionalism • Postmodernism • Deconstructivism • Modernism • Islamic • more....
- Architecture of the world Denmark • Germany • India • Madagascar • Norway • Russia • United Kingdom • United States • more....
- Awards Aga Khan Award • Driehaus Architecture Prize • International Architecture Awards • Pritzker Architecture Prize • more....
- Building science Architectural engineering • Earthquake engineering • Green building • Structural engineering • Acoustical engineering • Building defects • more....
- Construction Trades • Materials science • Project management • Project planning • more
- Landscape architecture Landscape architects • History • Desire lines • Energy-efficient landscaping • Greenway (landscape) • materials • Landscape design • Landscape maintenance • Landscape planning • Natural landscaping • Site planning • more....
- Law Contract law • Property law • Employment law • Land law • Tort • Equity
- Economics of Architecture Cost management • Quantity surveyor • Critical path analysis • Elemental cost planning • Cost–benefit analysis
- Planning and Urban design Topics • Zoning • Growth management • Land-use planning • New Urbanism • more....
- Architecture museums Shchusev Museum of Architecture • Museum of Finnish Architecture • German Architecture Museum
- By Year: 2015 in architecture • 2014 in architecture • 2013 in architecture • 2012 in architecture • 2011 in architecture • more....
- Vernacular architecture Timber framing • Thatching • Vernacular architecture of the Carpathians • Indian vernacular architecture • Vernacular architecture of Indonesia • Vernacular architecture in Norway • Open-air museum • Architecture of Samoa • Sasak architecture • Zakopane Style
Recognized content
Featured lists
|
|---|
|
Featured lists |
Featured pictures selections
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Major subcategories
| Architects | Architecture | Architectural elements | Architectural history | Buildings & structures |

|

|

|

| |
| Architecture by country | Construction | Landscape architecture | Structural engineering | Urban planning |
All categories
Things you can do
WikiProject Architecture

- Join the WikiProject.
- Improve: articles listed at Architecture pages needing attention
- Expand: stubs - Category:Architecture stubs - Category:Architect stubs - Category:Building and structure stubs
- Request an article: about a topic in architecture.
- Featured article candidates, Good article nominees, Articles for deletion, Requested moves
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus

![Image 1 The main entrance to Castell Coch Castell Coch (Welsh for 'Red Castle'; Welsh pronunciation: [ˈkas.tɛɬ koːχ]) is a 19th-century Gothic Revival castle built above the village of Tongwynlais in South Wales. The first castle on the site was built by the Normans after 1081 to protect the newly conquered town of Cardiff and control the route along the Taff Gorge. Abandoned shortly afterwards, the castle's earth motte was reused by Gilbert de Clare as the basis for a new stone fortification, which he built between 1267 and 1277 to control his freshly annexed Welsh lands. This castle may have been destroyed in the native Welsh rebellion of 1314. In 1760, the castle ruins were acquired by John Stuart, 3rd Earl of Bute, as part of a marriage settlement that brought the family vast estates in South Wales. John Crichton-Stuart, 3rd Marquess of Bute, inherited the castle in 1848. One of Britain's wealthiest men, with interests in architecture and antiquarian studies, he employed the architect William Burges to rebuild the castle, "as a country residence for occasional occupation in the summer", using the medieval remains as a basis for the design. Burges rebuilt the outside of the castle between 1875 and 1879, before turning to the interior; he died in 1881 and the work was finished by Burges's remaining team in 1891. Bute reintroduced commercial viticulture into Britain, planting a vineyard just below the castle, and wine production continued until the First World War. He made little use of his new retreat, and in 1950 his grandson, the 5th Marquess of Bute, placed it into the care of the state. It is now controlled by the Welsh heritage agency Cadw. (Full article...)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/d/d2/Blank.png)